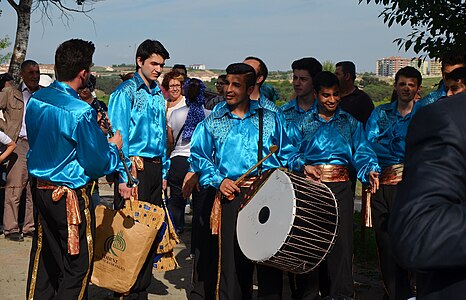Romani people in Turkey
Romanlar | |
|---|---|
| Total population | |
| around 500,000 | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Istanbul, East Thrace, Marmara Region, Aegean Region, İzmir Province | |
| Languages | |
| Turkish as first langugae, in lesser case Rumelian Turkish, nearly extinct Sepečides Romani and Rumelian Romani | |
| Religion | |
| Sunni Islam, Sufism of Qadiriyya - Tariqa | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Lom people, Dom people, Abdal of Turkey |
The Romani people in Turkey (Turkish: Türkiye'deki Romanlar) or Turks of Romani Background (Turkish: Roman kökenli Türk) are Turkish citizen and the biggest subgroup of the Turkish Roma, they are Sunni muslims, mostly of Sufism branch,[1] who speak Turkish as their first language, in their own accent, and take the Turkish culture, many deny their Romani Background over centuries in order to establish a Turkish Identity to become more recognized by the Host population and declare themselves to be Turks of Oghuz Turks Ancestry. Especially some of them claimed to be Members of the Yörüks, Amuca tribe, Gajal or Tahtacı.[2] In Turkey, since 1996, they named official as Romanlar and not as Roma. They are also called Şopar (Gypsy kid) in Rumelian Romani dialect or Manuş (Human), and Çingene (Gypsy) in Turkish, while once in Ottoman Turkish they was named Cingân (Gypsy), Kıptî (Copts) and Mısırlı (Egyptians).[3] As Gastarbeiter some Turkish Roma came to Germany and Austria and other European Countrys and fully assimilated in Turks in European communities.[4]
East Thrace, where the majority of the Romanlar live in, is nicknamed for fun "Gypsy County" by the Turks.[5]
There are officially about 500,000 Romani people in Turkey.[6][7][8][9]
History
There are records of the presence of Romani people from AD 800 in Thrace, known in Greek as Athinganoi. At the time of the Rome–Constantinople schism of 1054, Athinganoi, settled Outside the Walls of Constantinople. Later in Ottoman time this quarter was named Sulukule, it is said, it was the oldest Roma settlement in Europe.[10]
With the expansion of the Ottoman Empire, Turkish speaking Muslim Romani people settled in Rumelia (southeastern Europe) under Ottoman rule. The Ottoman Turkish Historian Evliya Çelebi explain in his Seyahatnâme, that Mehmed the Conqueror in 1453, take Muslim Roma from Balat, Didim and former Menteşe (beylik), also the irreligious Roma from Gümülcine, and settled them in Istanbul, but both Groups didn't get along well, and some of the Gümülcine Groups went back. He also wrote, that the language of the Roma früm Gümülcine have Banyan merchants roots.[11] The Ottoman Archives of the 18th century and 19th century told from 4 clans of the so-called Türkmen Kıpti, who speak Turkish only with few Romani words in there jargon and who are Alevis of Bektashi Order, as a separate group of other Roma people in Rumelia. They once migrated from Anatolia and settled finally in the Balkans and Crimea.[12][13] Uniquely to Ottoman history, the Muslim Roma people were given their own Sanjak at the Kırklareli Province, by the order of Suleiman the Magnificent at 1530. Until today the Turkish Roma see Thrace as there Homeland.[14] The Turkish Historian Reşat Ekrem Koçu, explained that Muslim (Horahane), Eastern Orthodox (Dasikane) and Pagan Roma (Gadjikane) Groups lived in the Ottoman Empire. He also explained that the Christian Lom people who lived in Istanbul convert closed to Islam in the 19th century[15]
Origin
The Romani people in Turkey are of very mixed Ancestry. According to their own oral tradition, (but it varies in some stories), their Ancestors once came from Hindustan[16][17] The Early Romani originate from the Indian subcontinent,[18][19][20][21][22][23] especially from Rohri in the Sukkur District of Sindh.[24] The linguistic evidence has indisputably shown that the roots of the Romani language lie in Central India: The language has grammatical characteristics of Indian languages and shares with them a big part of the basic lexicon, for example, body parts or daily routines.[25] More precisely, Romani shares the basic lexicon with Sanskrit and Prakrit.[26] In February 2016, during the International Roma Conference, the Indian Minister of External Affairs stated that the people of the Roma community were "children of India". The conference ended with a recommendation to the Government of India to recognize the Roma community, spread across 30 countries, as a part of the Indian diaspora.[27]
Genetic
Genetic findings in 2012 suggest the Early Romani originated in Indian subcontinent.,.[19][20][28] Another genetic study shows that Turkish Roma are related to the Changar tribe from Pakistan of Punjab,.[29] While the Early Romani people traces back to the Indian subcontinent,[30] also Gene flow from the Ottoman Turks spilled over and established a higher frequency of the Y-haplogroups J and E3b in Balkan Roma Groups.[31] The Greek Doctor A. G. Paspati made the statemant in his Book from 1860, that Turks married often Roma Woman,[32] as example are the Basketmaker (Sepetçi) Sepečides Romani who is of Turkish/Greeks mixed Ancestry.[33] Greeks and South Slavs DNA also influenced the Balkans Roma people.[34] Also, the genetics of Peoples of the Caucasus influenced the Genetic impact of Roma people.[35]
Migration to Turkey
During the Population exchange between Greece and Turkey in 1923, different Muslim Roma groups from Greece, like the Sepetčides (Basketmakers)[36] or the Tütünčides (Tobacco workers)[37] moved to Turkey, and called Mübadil Romanlar.[38] The Tobacco worker Roma from Greece, became active members in the Communist Party of Turkey (historical).[39]
Turkish speaking Muslim Roma from Bulgaria, went from 1878 - 1989 in weaves to Turkey together with Turks and Pomaks.[40] Especially Turkish speaking pipe and drum band tribes, descendants of the Turcoman Gypsys went after Bulgarian Declaration of Independence to Istanbul.[41]
In 1950-1951 Muslim Roma from Bulgaria came to Turkey and settled in Çanakkale and surroundings.[42]
From 1953 -1968, Muslim Roma and Turks from Yugoslavia emigrated to Turkey,[43][44]
Demographics
The majority of the Romani people in Turkey live in East Thrace, Marmara Region and Aegean Region. Cities with a high percentage of Romanlar are Edirne and Istanbul.[15]
Culture
The Turkified Romani speak Turkish as there first language and assimilated fully in Turkish culture and are Cultural Muslims, based on Sunni Islam in the Hanafi school, and practise male Religious male circumcision,[45] engagements and weddings on a grand scale. The burying foreskin after circumcision in a cemetery near or the Garden of a Mosque is a tradition amog the Muslim Roma. A foreskin is looked as unclean, and the Tradition of a Kirve, (Kirve is the godfather who pays for the celebrations), is taken by Alevism-Bektashism.[46] The Roma bands and their special music in 9/8 beat and songs are particularly well known in Turkey. The majority deny their Romani origins and describe themselves as Turks and are proud to say How happy is the one who says I am a Turk.[47] They see themselves as Turks and have the same cultural similarities with Turks, no similarities with Christian Roma from Europe.[48] Belly dance, performed by women and men. In Edirne, they hold the Kakava festival every year.[49]
Conservative romani groups are e.g. , the long-established Tekkekapılı, Kağıtçılar (Papermakers), the semi-nomadic Bandırmalı, (named after Bandırma, but their ancestors once came from Greece around 1923), who all live in Selamsız Romani-quarter in Üsküdar. The Kağıtçılar, in particular, have their own dialect that is not understood by other roma groups in their neighborhood.[50][51] Turkish-speaking Roma from Turkey distance themselves from other non-Turkish Roma groups, especially from Christian Roma, they call them Yabancı (foreigners). While Christian Roma regard them simple as Turks (term for Muslims), because they have no Romanipen.[52]
Legal status
In modern Turkey, Muslim Romani do not have the legal status of an ethnic minority because they are traditionally adherents of the Islamic faith, adherents of which, regardless of ethnicity or race, are considered part of the ethnic majority in Turkey. This goes as far back as the Treaty of Lausanne (1923), in which Section III "Protection of Minorities" puts an emphasis on non-Muslim minorities.[53]
In popular culture
A group of Turkish Romani appears in the 16th century Ottoman Constantinople of the video game Assassin's Creed: Revelations.
A Turkish TV series made between 2004 and 2007 called "Cennet Mahallesi" is based on Istanbulite Romans.
Sufism
Many Turkish Roma, are members of the Hindiler Tekkesi a Qadiriyya-Tariqa, founded in 1738 by the Indian Muslim Sheykh Seyfullah Efendi El Hindi in Selamsız.[1]
Groups of Turkish Romanlar
Yerli and Çerge generic term
The majority of the Romani people in Turkey live in Eastern Thrace, mostly in the Kırklareli Province, they are divided into two Main groups, the Sedentary Yerli and the Semi-Nomadic Çerge. There are several subgroups of both, named after their old professions which they once practiced or which they still do in part, as example: the Sepetçiler (Basketmaker's), Çiçekçi (Flower seller), Cambazı (Horse trader), Ayıcılar (Bear-leader's), Demirci (Blacksmith), Çiçekçi (Flower seller), Sünnetçi (Circumciser), Subaşı (Water carrier), Kuyumcu (Goldsmith), Kalaycı (Tinsmith), Şarkıcı (Singer), Müzisyen (Musician), Elekçiler (Sieve maker's), Bohçacı (Bundler), Arabacı (Coachman), Katırcıları (Muleteer's), etc. However, mostly all of the different Romani groups today are Working poor in a wide variety of jobs. The Yerli and the Çerge, live together in the Mahalla, but they don't like each other. The Yerli speak only Turkish as their mother tongue, while the Çerge speak Turkish and Rumelian Romani.[54] Although both groups are Muslims, the Yerli look down on the Çerge, and consider them savage, uncivilized and keep their distance from them. Interestingly, the Yerli call themselves Romanlar, while they call the Çerge Çingeneler. The Yerli consider the Çerge to have once come from the Balkans to Eastern Thrace.[55]
Sepetçi subgroup
Since Ottoman Empire, the Muslim basket weavers Romanlar were very respected alongside Roma musicians. Because those Romani people, who became Muslims after the conquest of Istanbul at 1453, set up the mehter band of the Ottoman military band and the best and richest basket makers of Istanbul came from Sulukule. The Basketmakers' Kiosk was also built in their honor, where the basket makers guild was based.[56] In East Thrace, the European part of turkey, in the Kırklareli Province,they are the Sepetçi Romanlar (Basket-weaver Roma), who are still doing their old job today and The Sepetçi Association was established in the Vize district of Kırklareli.[57] Also in Gelibolu they are a Group of Sepetçi whose Nomad Ancestor's came from Thessaloniki/Selanik in Greece, still weave Baskets.[58] Also in other parts in Turkey, live descendants of the Basketmaker Roma, who once came from Greece, some of them still speak Sepečides Romani.
Ayjides subgroup
The Ayjides or Ayıcı are former Bear-leader's who hold Tame bear's until the 1990s,.[59][60]
Romani Heritage
Trough the World Romani Congress and contact with other Romani groups of different countrys, the interest in their own Romani Heritage and Language awakened, by the Romanlar in Turkey.[61][62] Only a view Romanlar in East Thrace use Sedentary Rumelian Romani dialect at Home together,[63] also the Sepečides Romani language in Izmir are nearly lost[64]
Gallery
A dancing bear around 1970 in Samsun. His holder beats the frame drum Def.
Romani in Istanbul in 2008.
Children in Ortaköy in Istanbul, 2000.
Notable Turkish people of Romani heritage
- Sibel Can, folk pop and classical music singer
- Didem, belly dancer, model and singer
- Kibariye, Arabesque-pop singer
- Özcan Purçu, politician
- Hüsnü Şenlendirici, musician
- Selim Sesler, clarinet virtuoso
- Ankaralı Turgut, musician
- Rafet el Roman, Popstar
See also
References
- ^ a b https://acikbilim.yok.gov.tr/bitstream/handle/20.500.12812/209305/yokAcikBilim_10317583.pdf?sequence=-1&isAllowed=y[bare URL PDF]
- ^ Kolukirik, Suat; Toktaş, Şule (2007). "Turkey's Roma: Political participation and organization". Middle Eastern Studies. 43 (5): 761–777. doi:10.1080/00263200701422675. S2CID 143772218 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ "Mehr als nur Roman Havası - Roma in der Türkei". 8 April 2019.
- ^ https://www.coe.int/t/dg4/education/roma/Source/RomaniEurope_EN.pdf[bare URL PDF]
- ^ "The Perception of Gypsies in Turkish Society - European Roma Rights Centre". Archived from the original on 2021-07-10. Retrieved 2021-12-24.
- ^ "UNHCR - Document Not Found". Archived from the original on 2012-10-10. Retrieved 2014-06-17.
- ^ Schleifer, Yigal (21 July 2005). "Roma Rights Organizations Work to Ease Prejudice in Turkey". Eurasianet.org. Archived from the original on 24 December 2013. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-07-29. Retrieved 2010-02-15.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Radikal-çevrimiçi / Türkiye / Romanlar 'Biz de varız!' diyor". Archived from the original on 2012-10-20. Retrieved 2010-03-24.
- ^ "Byzanz [Rombase]".
- ^ "THE GYPSIES OF ISTANBUL | History of Istanbul".
- ^ Marushiakova; Popov, Vesselin (2014). "Migrations and Identities of Central Asian 'Gypsies'" – via ResearchGate.
- ^ Yılgür, Egemen (2021). "Turcoman Gypsies in the Balkans: Just a Preferred Identity or More?". In Ki︠u︡Chukov, Khristo; Zakhova, Sofii︠a︡; Dumunica, Ian; Duminica, Ion (eds.). Romani History and Culture: Festschrift in Honour of Prof. Dr. Vesselin Popov. ISBN 9783969390719 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ https://rm.coe.int/ottoman-empire-factsheets-on-romani-history/16808b193d[bare URL PDF]
- ^ a b "THE GYPSIES OF ISTANBUL | History of Istanbul".
- ^ "ÇİNGENELER - TDV İslâm Ansiklopedisi".
- ^ "Roman Ruhu - Turkish Roma". YouTube.
- ^ Hancock, Ian F. (2005) [2002]. We are the Romani People. Univ of Hertfordshire Press. p. 70. ISBN 978-1-902806-19-8: ‘While a nine century removal from India has diluted Indian biological connection to the extent that for some Romani groups, it may be hardly representative today, Sarren (1976:72) concluded that we still remain together, genetically, Asian rather than European’
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ a b Mendizabal, Isabel (6 December 2012). "Reconstructing the Population History of European Romani from Genome-wide Data". Current Biology. 22 (24): 2342–2349. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2012.10.039. PMID 23219723.
- ^ a b Sindya N. Bhanoo (11 December 2012). "Genomic Study Traces Roma to Northern India". The New York Times.
- ^ Current Biology.
- ^ K. Meira Goldberg; Ninotchka Devorah Bennahum; Michelle Heffner Hayes (2015-10-06). Flamenco on the Global Stage: Historical, Critical and Theoretical Perspectives. p. 50. ISBN 9780786494705. Retrieved 2016-05-21.
- ^ Simon Broughton; Mark Ellingham; Richard Trillo (1999). World Music: Africa, Europe and the Middle East. Rough Guides. p. 147. ISBN 9781858286358. Retrieved 2016-05-21.
Roma Rajastan Penjab.
- ^ "HYDERABAD: Gypsies hail from Sindh, claims Dr Kazi". 25 September 2006.
- ^ Šebková, Hana; Žlnayová, Edita (1998), Nástin mluvnice slovenské romštiny (pro pedagogické účely) (PDF), Ústí nad Labem: Pedagogická fakulta Univerzity J. E. Purkyně v Ústí nad Labem, p. 4, ISBN 978-80-7044-205-0, archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04
- ^ Hübschmannová, Milena (1995). "Romaňi čhib – romština: Několik základních informací o romském jazyku". Bulletin Muzea Romské Kultury. Brno (4/1995).
Zatímco romská lexika je bližší hindštině, marvárštině, pandžábštině atd., v gramatické sféře nacházíme mnoho shod s východoindickým jazykem, s bengálštinou.
- ^ "Can Romas be part of Indian diaspora?". Khaleejtimes.com. 29 February 2016. Retrieved 4 March 2016.
- ^ "5 Intriguing Facts About the Roma". Live Science. 23 October 2013.
- ^ Adnan, Atif; Rakha, Allah; Lazim, Hayder; Nazir, Shahid; Al-Qahtani, Wedad Saeed; Abdullah Alwaili, Maha; Hadi, Sibte; Wang, Chuan-Chao (2022). "Are Roma People Descended from the Punjab Region of Pakistan: A Y-Chromosomal Perspective" (PDF). Genes. 13 (3): 532. doi:10.3390/genes13030532. PMC 8951058. PMID 35328085.
- ^ Melegh, Bela I.; Banfai, Zsolt; Hadzsiev, Kinga; Miseta, Attila; Melegh, Bela (2017). "Refining the South Asian Origin of the Romani people". BMC Genetics. 18 (1): 82. doi:10.1186/s12863-017-0547-x. PMC 5580230. PMID 28859608 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ Bánfai, Zsolt; Melegh, Béla I.; Sümegi, Katalin; Hadzsiev, Kinga; Miseta, Attila; Kásler, Miklós; Melegh, Béla (13 June 2019). "Revealing the Genetic Impact of the Ottoman Occupation on Ethnic Groups of East-Central Europe and on the Roma Population of the Area". Frontiers in Genetics. 10: 558. doi:10.3389/fgene.2019.00558. PMC 6585392. PMID 31263480.
- ^ Paspati, A. G.; Hamlin, C. (1860). "Memoir on the Language of the Gypsies, as Now Used in the Turkish Empire". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 7: 143–270. doi:10.2307/592158. JSTOR 592158.
- ^ http://rombase.uni-graz.at/cd/data/ethn/groupsat/data/sepecides.en.pdf[bare URL PDF]
- ^ Martínez-Cruz, Begoña; Mendizabal, Isabel; Harmant, Christine; De Pablo, Rosario; Ioana, Mihai; Angelicheva, Dora; Kouvatsi, Anastasia; Makukh, Halyna; Netea, Mihai G.; Pamjav, Horolma; Zalán, Andrea; Tournev, Ivailo; Marushiakova, Elena; Popov, Vesselin; Bertranpetit, Jaume; Kalaydjieva, Luba; Quintana-Murci, Lluis; Comas, David (2016). "Origins, admixture and founder lineages in European Roma". European Journal of Human Genetics. 24 (6): 937–943. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2015.201. PMC 4867443. PMID 26374132 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ Bánfai, Zsolt; Ádám, Valerián; Pöstyéni, Etelka; Büki, Gergely; Czakó, Márta; Miseta, Attila; Melegh, Béla (2018). "Revealing the impact of the Caucasus region on the genetic legacy of Romani people from genome-wide data". PLOS ONE. 13 (9): e0202890. Bibcode:2018PLoSO..1302890B. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0202890. PMC 6130880. PMID 30199533 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ "Sepečides / Sevlengere Roma".
- ^ "Figure 3. The Roma tobacco workers who live in Ortaköy/Beşiktaş with".
- ^ "Unutulan Mübadil Romanlar: 'Toprağın kovduğu insanlar'". 7 February 2021.
- ^ Yilgür, Egemen (2015). "Ethnicity, class and politicisation: Immigrant Roma tobacco workers in Turkey". Romani Studies. 25 (2): 167–196. doi:10.3828/rs.2015.7. S2CID 146293564 – via ResearchGate.
- ^ Maeva, Mila. "(PDF) Маева, М. Българските турци-преселници в Р Турция (култура и идентичност). 2005. Bulgarian Turks - Emigrants in Turkey (Culture and Identity). София: IMIR. | Mila Maeva - Academia.edu".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Yılgür, Egemen (January 2021). "Turcoman Gypsies in the Balkans: Just a Preferred Identity or More?". Romani History and Culture Festschrift in Honour of Prof. Dr. Veselin Popov / Hristo Kyuchukov, Sofiya Zahova, Ian Duminica.
- ^ https://www.acarindex.com/pdfler/acarindex-4982-5629.pdf[bare URL PDF]
- ^ https://www.etd.ceu.edu/2012/rajkovic_nikolina.pdf[bare URL PDF]
- ^ Pezo, Edvin (2018). "Emigration and Policy in Yugoslavia: Dynamics and Constraints within the Process of Muslim Emigration to Turkey during the 1950s". European History Quarterly. 48 (2): 283–313. doi:10.1177/0265691418757391. S2CID 149846476.
- ^ Barutcu, Atilla (January 2015). ""Ucundan Azıcık"la Atılan Sağlam Temel: Türkiye'de Sünnet Ritüeli ve Erkeklik İlişkisi". Masculinities: A Journal of Identity and Culture.
- ^ "Circumcision in Turkey - Turkey Cultural Tour".
- ^ Ülker, Erol (11 January 2008). "Assimilation of the Muslim communities in the first decade of the Turkish Republic (1923-1934)". European Journal of Turkish Studies. Social Sciences on Contemporary Turkey. doi:10.4000/ejts.822.
- ^ http://www.errc.org/uploads/upload_en/file/03/37/m00000337.pdf[bare URL PDF]
- ^ Elena Marushiakova, Veselin Popov (2001) "Gypsies in the Ottoman Empire", ISBN 1902806026University of Hertfordshire Press
- Original: Елена Марушиакова, Веселин Попов (2000) "Циганите в Османската империя". Литавра, София (Litavra Publishers, Sofia).(in Bulgarian)
- ^ "Home".
- ^ "Home".
- ^ Ozatesler, G.; Özate?Ler, Gül (11 February 2014). Gypsy Stigma and Exclusion in Turkey, 1970: The Social Dynamics of Exclusionary Violence. ISBN 9781137386618.
- ^ "Treaty of Lausanne - World War I Document Archive". Lib.byu.edu. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ https://humstatic.uchicago.edu/slavic/archived/papers/Friedman-OldestBalkRmiw-BDankoff.pdf[bare URL PDF]
- ^ https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/download/article-file/751137[bare URL PDF]
- ^ "SEPETÇILIK - Definition und Synonyme von sepetçilik im Wörterbuch Türkisch".
- ^ "Vize'de Sepetçi Romanları Derneği açılışına ilgi".
- ^ "Sepetçiler ata mesleğini devam ettirme çabasında".
- ^ "Ayjides".
- ^ "Et tu, 'Brütüs': Last dancing bear in Turkey dies in shelter". Daily Sabah. 27 November 2021.
- ^ "Roma living in Turkey's southern Mersin province publish first Roma-Turkish dictionary". Daily Sabah. 3 May 2016.
- ^ https://etd.lib.metu.edu.tr/upload/1252683/index.pdf[bare URL PDF]
- ^ "Rumelian Sedentary: Dialect Sampler, Romani Dialects Interactive - ROMANI Project Manchester".
- ^ http://rombase.uni-graz.at/cd/data/ethn/groupsat/data/sepecides.en.pdf[bare URL PDF]
External links
![]() Media related to Romani people in Turkey at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Romani people in Turkey at Wikimedia Commons
- All articles with bare URLs for citations
- Articles with bare URLs for citations from August 2022
- Articles with PDF format bare URLs for citations
- Articles with bare URLs for citations from March 2022
- CS1 maint: archived copy as title
- CS1 maint: postscript
- Articles with bare URLs for citations from June 2022
- CS1 errors: missing periodical
- Articles with Bulgarian-language sources (bg)
- Articles with short description
- Short description with empty Wikidata description
- "Related ethnic groups" needing confirmation
- Articles using infobox ethnic group with image parameters
- Pages using collapsible list with both background and text-align in titlestyle
- Articles containing Turkish-language text
- Articles needing cleanup from August 2022
- Commons category link is defined as the pagename
- Romani in Turkey