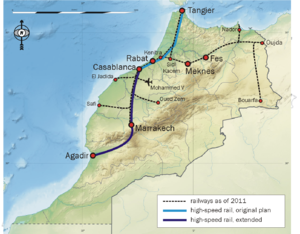
Casablanca–Tangier high-speed rail line
| Al Boraq | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 An ONCF Al Boraq Alstom RGV2N2 high-speed trainset at the Tanger-Ville railway station, November 2018 | |||
| Overview | |||
| Native name | البُراق | ||
| Status | Active | ||
| Owner | Morocco | ||
| Locale | Morocco | ||
| Termini |
| ||
| Service | |||
| Operator(s) | ONCF | ||
| Rolling stock | Alstom Euroduplex | ||
| History | |||
| Opened | 15 November 2018[1] | ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 323 km (201 mi) | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| Electrification |
| ||
| Operating speed | 320 km/h (200 mph) | ||
| |||
Al Boraq (Arabic: البُراق)[2] is a 323-kilometre-long (201 mi) high-speed rail service between Casablanca and Tangier, operated by ONCF in Morocco. The first of its kind on the African continent, the high-speed service was inaugurated on 15 November 2018 by King Mohammed VI of Morocco, following over a decade of planning and construction by Moroccan national railway company ONCF. It is the first phase of a planned 1,500 kilometres (930 mi) high-speed rail network in Morocco.[3] Al Boraq trains operate over a dedicated high speed line, reaching speeds of up to 320 km/h on the 186 km sector between Tangier and Kenitra. From Kenitra, trains operate over an upgraded mainline for the final 137 km through Morocco’s most populous corridor, passing through Rabat to Casablanca.[4]
Name
King Mohammed VI named the high-speed service Al Boraq (البُراق) in reference to the creature in Islamic tradition believed to have transported some prophets,[5] notably the prophet Muhammad from Mecca to Jerusalem during the night journey.
History
Early studies into the feasibility of high-speed rail in Morocco began in 2003, and by 2006 the route between Tangier and Kenitra had been identified as being among the first lines to be constructed.[6] In 2007, preliminary agreements to manage the project had been signed, and ONCF announced plans to purchase 18 Alstom trainsets.[6][7] In 2008, ONCF said that it planned to begin construction that year, with operations to begin in 2013.[6]
Financing was not finalised until February 2010, when ONCF signed agreements worth 20 billion dirhams (DH).[8] Direct investments came from the Moroccan government, which allocated DH4.8 billion to the project, and European sources, which invested a total of DH1.9 billion, while the remaining DH12.3 billion came from commercial loans.[8] DH10 billion were to be spent on infrastructure, with DH5.6 billion going to supporting equipment and DH4.4 billion to rolling stock.[8] At the time, work was expected to start in mid-2010, with service beginning in December 2015.[8] In December 2010, ONCF signed a final agreement to purchase 14 Alstom Euroduplex trainsets.[9] Following further delays, construction of the line began on 29 September 2011, when a groundbreaking ceremony took place in Tangier.[10]
On 25 September 2012, work began on a project to increase capacity on the trackage between Kenitra and Casablanca by constructing a dedicated freight track in the existing right of way, allowing for passenger trains to access Casablanca from the high-speed line to Tangier.[11] In addition to the rail construction, stations in four locations (Tangiers, Kenitra, Rabat/Agdal, and Casablanca) were either constructed from the ground up or rebuilt from existing facilities.[12] On 19 June 2015, rolling stock deliveries began with the arrival of the first trainset in Tangier.[13] In September, the service facility for the trains in Tangier was completed and a joint venture between ONCF and French rail operator SNCF was established to maintain the trains for a 15-year contract.[14] In February 2017, testing of the trains at revenue speeds began; during the test program, an African rail speed record of 357 kilometres per hour (222 mph) was set.[12]
In October 2017, track construction was completed, followed by installation of the new electric catenary that November.[3] The electrical system was energised for the first time in January 2018, and the line's control facility came online the following month.[3] By mid-2018, the stations had been completed, though the expected entry into service was pushed back to the end of the year, as trial runs over the route had yet to be operated.[3][12]
On 15 November 2018, the Al Boraq service was inaugurated at a Tangier ceremony on a special train that traveled to Rabat; revenue service was to begin by the end of the year.[5] By December 25, 2018, trains were scheduled to depart Casablanca every two hours from 06:00 until 21:00.
The inauguration of the high-speed rail service also came with the opening of several new or renovated train stations: Tanger-Ville Railway Terminal,[15] Kenitra Station,[16] Rabat-Agdal Station,[17] and Casa-Voyageurs Railway Station.[18]
Infrastructure
The line is made up of two sections—a new route from Tangier to Kenitra and an upgrade of the existing route from Kenitra to Casablanca.[10] The 186-kilometre-long (116 mi) Tangier–Kenitra line has a top speed of 320 kilometres per hour (200 mph), while the 137-kilometre-long (85 mi) Kenitra–Casablanca line was rated for 160 kilometres per hour (99 mph) when service began, with a planned upgrade to 220 kilometres per hour (140 mph).[5] The trackage from Kenitra to Casablanca is to be eventually replaced by a new high-speed right of way, with construction scheduled to begin in 2020.[5] Two electrification types are used—from Tangier to Kenitra, the new trackage was built with 25 kV at 50 Hz, while the line from Kenitra to Casablanca retained the existing 3 kV DC catenary.[5] The ETCS-type signal system was installed by Ansaldo STS and Cofely Ineo.[19]
At service launch in 2018, travel time between Casablanca and Tangier dropped from 4 hours and 45 minutes to 2 hours and 10 minutes.[5] Completion of dedicated high-speed trackage to Casablanca would further reduce travel time to 1 hour and 30 minutes.[5]
Rolling stock
The twelve (14 were originally ordered) Alstom Euroduplex trainsets operating on the line are bilevel and have a passenger capacity of 533.[9][5] Each trainset is composed of two power cars and eight passenger cars (two first-class cars, five second-class cars, and a buffet car).[9]
Gallery
See also
References
- ^ "'Africa's fastest train' steams ahead in Morocco". Al Jazeera. 15 November 2018. Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- ^ "صاحب الجلالة الملك محمد السادس يتفضل ويطلق إسم "البراق" على القطار المغربي الفائق السرعة". Maroc.ma (in Arabic). 12 July 2018. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ^ a b c d "ONCF prepares for launch of high-speed services". International Rail Journal. 12 March 2018. Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- ^ "TrainReview's guide to Morocco's Al-Boraq high speed train".
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Africa's first high speed line inaugurated". Railway Gazette International. 16 November 2018. Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- ^ a b c "Work on Tanger - Kénitra high speed line to start soon". Railway Gazette International. 14 May 2008. Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- ^ "Morocco to order Duplex TGVs". Railway Gazette International. 23 October 2007. Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- ^ a b c d "High speed funding package agreed". Railway Gazette International. 18 February 2010. Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- ^ a b c "ONCF to buy 14 Duplex high speed trains". Railway Gazette International. 10 December 2010.
- ^ a b "Ceremony launches Tanger – Casablanca high speed project". Railway Gazette International. 29 September 2011.
- ^ "Casablanca – Kénitra upgrading starts". Railway Gazette International. 26 September 2012. Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- ^ a b c "Morocco's Al Boraq high speed service to launch by year end". Railway Gazette International. 30 July 2018. Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- ^ "Africa's first high speed train delivered". Railway Gazette International. 1 July 2015. Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- ^ "Tanger high speed train depot inaugurated". Railway Gazette International. 21 September 2015. Retrieved 21 November 2018.
- ^ "محطة القطار بطنجة تفتح أبوابها استعدادا لإنطلاق البراق". طنجة 24 (in Arabic). 19 November 2018. Retrieved 2 March 2020.
- ^ "محطة القطار في القنيطرة تنتزع "جائزة فرساي"". Hespress (in Arabic). 14 September 2019. Retrieved 2 March 2020.
- ^ "المغرب وفرنسا يدشنان "البراق".. أسرع قطار في أفريقيا". www.aljazeera.net (in Arabic). Retrieved 2 March 2020.
- ^ "فيديو: افتتاح محطة القطار الجديدة بتمارة بتكلفة 36 مليون درهم". 2M (in Arabic). Retrieved 2 March 2020.
- ^ "Tanger - Kénitra high speed line signalling contract signed". Railway Gazette International. 4 April 2013. Retrieved 5 April 2013.