Trimethylplatinum iodide
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Iodotrimethylplatinum(IV)
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| Properties | |
| C12H36I4Pt4 | |
| Molar mass | 1468.374 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 190-195 °C |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H228, H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H413 | |
| P210, P240, P241, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P370+P378, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
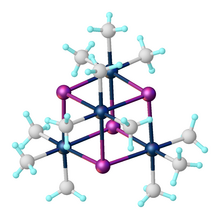
Trimethylplatinum iodide is the organoplatinum complex with the formula [(CH3)3PtI]4. It is a white, air-stable solid that was one of the first organometallic complexes reported. It arises from the reaction of potassium hexachloroplatinate with methylmagnesium iodide.[1] The complex exists as a tetramer: a cubane-type cluster with four octahedral Pt(IV) centers linked by four iodides as triply bridging ligands.[2]
The complex undergoes diverse reactions involving cleaving Pt-I bridges. Derived complexes include (CH3)3PtI(bipy) and (CH3)3PtI(NH3)2. Replacement of the iodide with hydroxide gives [(CH3)3PtOH]4.
References
- ^ Baldwin, J. C.; Kaska, W. C. (1975). "Improved Isolation Procedure for the Preparation of Iodo(trimethyl)platinum(IV)". Inorg. Chem. 14 (8): 2020. doi:10.1021/ic50150a063.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - ^ Ebert, K. H.; Massa, W.; Donath, H.; Lorberth, J.; Seo, B. S.; Herdtweck, E. (1998). "Organoplatinum Compounds: VI. Trimethylplatinum Thiomethylate and Trimethylplatinum Iodide. The Crystal Structures of [(CH3)3PtS(CH3)]4 and [(CH3)3PtI]4·0.5CH3I". J. Organomet. Chem. 559 (1–2): 203–207. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(98)00414-8.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
Categories:
- CS1 maint: uses authors parameter
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Chembox having GHS data
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Articles with short description
- Short description with empty Wikidata description
- Organoplatinum compounds
- Iodo complexes