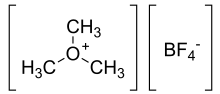
Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate
| |
| Other names
Trimethyloxonium fluoroborate
Meerwein's salt | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H9BF4O | |
| Molar mass | 147.91 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 179.6–180 °C (355.3–356.0 °F; 452.8–453.1 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is the organic compound with the formula (CH3)3OBF4. (It is sometimes called "Meerwein's salt" after Hans Meerwein.[1][2]) This salt is a strong methylating agent, being a synthetic equivalent of CH+3. It is a white solid that rapidly degrades upon exposure to atmospheric moisture, although it is robust enough to be weighed quickly without inert atmosphere protection. Triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is a closely related compound.
Preparation and reactions
The compound is prepared by the reaction of boron trifluoride with dimethyl ether and epichlorohydrin:[1]
- 4 Me2O·BF3 + 2 Me2O + 3 C2H3(O)CH2Cl → 3 Me3O+BF−4 + B[(OCH(CH2Cl)CH2OMe]3
The salt hydrolyzes readily:
- Me3OBF4 + H2O → Me2O + MeOH + HBF4
Trimethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate is generally ranked as the strongest commercially available reagent for electrophilic methylation, being stronger than methyl sulfonate esters, including methyl triflate and methyl fluorosulfonate ("magic methyl").[3] Only the exotic dimethylhalonium reagents (Me2X+SbF−6, X = Cl, Br, I), methyl carboranate reagents, and the transiently-generated methyldiazonium cation (MeN+2) are stronger sources of electrophilic methyl.
Due to its high reactivity, it is rapidly destroyed by atmospheric moisture and best stored in an inert atmosphere glovebox at −20 °C. Its degradation products are corrosive, although it is considerably less hazardous than methyl triflate or methyl fluorosulfonate, on account of its lack of volatility.
References
- ^ a b T. J. Curphey (1988). "Trimethyloxonium Tetrafluoroborate". Organic Syntheses.; Collective Volume, vol. 6, p. 1019
- ^ Meerwein's salt classically referred to triethyloxonium tetrafluoroborate. However, in recent years, the trimethyloxonium salt has also been called Meerwein's salt.
- ^ Stang, Peter J.; Hanack, Michael; Subramanian, L. R. (1982). "Perfluoroalkanesulfonic Esters: Methods of Preparation and Applications in Organic Chemistry". Synthesis. 1982 (2): 85–126. doi:10.1055/s-1982-29711. ISSN 0039-7881.
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Pages using collapsible list with both background and text-align in titlestyle
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chembox image size set
- Articles with short description
- Short description with empty Wikidata description
- Methylating agents
- Tetrafluoroborates
- Oxycations
- Oxonium compounds