Nephilengys malabarensis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Nephilengys malabarensis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Araneae |
| Infraorder: | Araneomorphae |
| Family: | Araneidae |
| Genus: | Nephilengys |
| Species: | N. malabarensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Nephilengys malabarensis (Walckenaer, 1842)[1]
| |
| |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Nephilengys malabarensis is an araneid spider.[1]
Females reach a body length of about 15 millimetres (0.59 in). The legs and palp are annulated yellow and black. Male body size less than 5 millimetres (0.20 in), with mostly grey-black legs.[2]
N. malabarensis is being preyed upon by the spider-eating jumping spider Portia.[2]
Name
The species name malabarensis refers to the Malabar coast of southern India, where it was first found.
Distribution
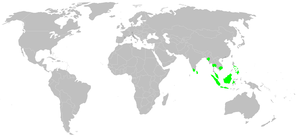
N. malabarensis occurs in South, South-East and East Asia from India and Sri Lanka to the Philippines, north to Yunnan, China, north-east to Saga and Kompira, Japan and east to Ambon Island of Indonesia. It is common at human dwellings and less common in rainforest. The Niah population inhabits cave entrances.[2]
References
- ^ a b c "Taxon details Nephilengys malabarensis (Walckenaer, 1841)". World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern. Retrieved 2017-05-16.
- ^ a b c Matjaž Kuntner (2007). "A monograph of Nephilengys, the pantropical 'hermit spiders' (Araneae, Nephilidae, Nephilinae)". Systematic Entomology. 32 (1): 95–135. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3113.2006.00348.x. S2CID 84146620.
Further reading
- Kralj-Fišer, S.; Kuntner, M. (2011). "Eunuchs as better fighters?". Naturwissenschaften. 99 (2): 95–101. Bibcode:2012NW.....99...95K. doi:10.1007/s00114-011-0873-1. PMID 22167072. S2CID 14727700.Error: "Q2182527" is not a valid Wikidata entity ID.
Categories:
- Articles with short description
- Short description with empty Wikidata description
- Articles with 'species' microformats
- Taxonbars desynced from Wikidata
- Taxonbar pages requiring a Wikidata item
- Taxonbars with invalid from parameters
- Taxonbars without secondary Wikidata taxon IDs
- Araneidae
- Spiders of Asia
- Spiders described in 1842