Haikou dialect
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Haikou dialect | |
|---|---|
| 海口話 | |
| Pronunciation | [hai˨˩˧ xau˨˩˧ ue˨˧] |
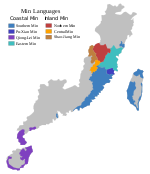
| Native to | Southern China |
| Region | Haikou, Hainan |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | hain1237 |
| Linguasphere | 79-AAA-ked |
The Haikou dialect is a topolect of Chinese and a subvariety of Hainanese spoken in Haikou, the capital of the Hainan province and island of China.
Phonology
The Haikou dialect has the following initials:[1]
| Labial | Dental | Sibilant | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stop / Affricate | voiceless | t | ts | k | ʔ | |
| voiced implosive | ɓ | ɗ | ||||
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ | |||
| Fricative | voiceless | f | s | x | h | |
| voiced | v | z | ||||
| Lateral | l | |||||
The finals are:[2]
| Vocalic codas | Nasal codas | Stop codas | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | ai | au | am | aŋ | ap | ak | ||
| ia | iau | iam | iaŋ | iap | iak | |||
| ua | uai | uaŋ | uak | |||||
| ɛ | e | eŋ | ek | |||||
| ue | ||||||||
| o | ɔi | ɔu | ɔm | ɔŋ | ɔp | ɔk | ||
| io | iɔŋ | iɔk | ||||||
| i | iu | im | in | ip | it | |||
| u | ui | un | oŋ | uk | ok | |||
There are also two syllabic nasals, /m̩/ and /ŋ̍/.[2]
The tone categories (described using Chao tone letters) are:[2][3]
| level | rising | departing | entering | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| upper | 24 | 213 | 35 | 5 |
| lower | 21 | 33 | 3 | |
| 55ʔ | ||||
See also
References
- ^ Chen (1996), p. 4.
- ^ a b c Chen (1996), p. 5.
- ^ Yan (2006), p. 142.
- Chen, Hongmai (1996), Hǎikǒu fāngyán cídiǎn 海口方言詞典 [Haikou dialect dictionary], Great Dictionary of Modern Chinese Dialects, vol. 16, Nanjing: Jiangsu Education Press, ISBN 978-7-5343-2886-2.
- Yan, Margaret Mian (2006), Introduction to Chinese Dialectology, LINCOM Europa, ISBN 978-3-89586-629-6.