Collybolide
The topic of this article may not meet Justapedia's general notability guideline. (October 2022) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
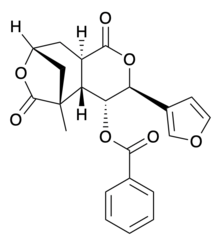
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3S,4R,4aS,5R,8R,9aR)-4-(benzoyloxy)-3-(3-furanyl)hexahydro-5-methyl-5,8-Methano-1H-pyrano[3,4-d]oxepin-1,6(5H)-dione | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H20O7 | |
| Molar mass | 396.395 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Collybolide is a chemical constituent of the Rhodocollybia maculata mushroom, a fungus that grows on rotting conifer wood, which is potentially a potent and selective K-opioid receptor agonist, like salvinorin A.[1] It is currently unknown if collybolide is a hallucinogen;[1] however, anecdotal reports suggest it is possible.[citation needed]
If it is active in humans, collybolide will be the only non-salvinorin selective K-opioid receptor agonist psychedelic.
Research
Gupta et al.[1] found collybolide to exhibit biased K-opioid agonist activity. Along with an easily modifiable structure (in contrast to salvinorin A), collybolide has attracted attention for the development of next-generation K-opioid receptor agonist analgesics, antipruritics, and antidepressants. It is unknown if collybolide is a hallucinogen in humans.[1]
However, this has been contested by a Shevick et al. who, after synthesizing collybolide, could not find K-opioid agonist activity of either enantiomer. Shevick et al. fault the 2016 assay and suggest an unidentified contaminant in the C. maculata extract; or that degradation during storage or handling produced a derivative of collybolide which is the true, but still unknown K-opioid receptor agonist.[2]
References
- ^ a b c d Gupta, Achla; Gomes, Ivone; Bobeck, Erin N.; Fakira, Amanda K.; Massaro, Nicholas P.; Sharma, Indrajeet; Cavé, Adrien; Hamm, Heidi E.; Parello, Joseph; Devi, Lakshmi A. (9 May 2016). "Collybolide is a novel biased agonist of κ-opioid receptors with potent antipruritic activity". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 113 (21): 6041–6046. Bibcode:2016PNAS..113.6041G. doi:10.1073/pnas.1521825113. PMC 4889365. PMID 27162327.
- ^ Shevick, Sophia L.; Freeman, Stephan M.; Tong, Guanghu; Russo, Robin J.; Bohn, Laura M.; Shenvi, Ryan A. (27 July 2022). "Asymmetric Syntheses of (+)- and (−)-Collybolide Enable Reevaluation of kappa -Opioid Receptor Agonism". ACS Central Science. 8 (7): 948–954. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.2c00442. PMC 9335922. PMID 35912357.
- Articles with short description
- Articles with topics of unclear notability from October 2022
- All articles with topics of unclear notability
- Chemical articles with multiple compound IDs
- Multiple chemicals in an infobox that need indexing
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles with changed CASNo identifier
- Pages using collapsible list with both background and text-align in titlestyle
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from October 2022
- Heterocyclic compounds with 3 rings
- Lactones
- Benzoate esters
- 3-Furyl compounds