Bruneian Sultanate (1368–1888)
Sultanate of Brunei | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1368–1888 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Flag | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
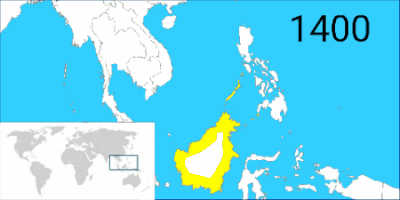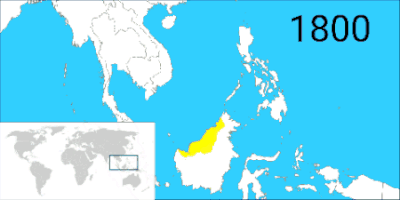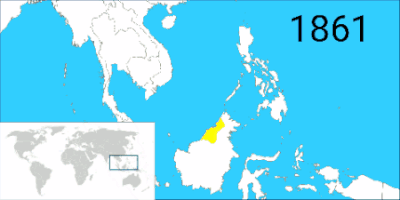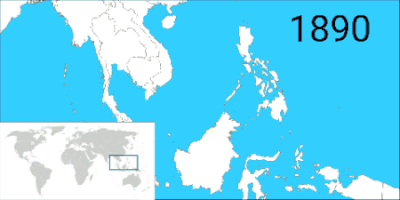
 The maximum territorial extent of the Bruneian Empire (yellow) with its vassals (light yellow) in 1521. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common languages | Brunei Malay, Old Malay, Old Tagalog, Arabic and Bornean languages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Bruneian | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sultans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1368–1402 | Sultan Muhammad Shah | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1425–1432 | Sharif Ali | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1485–1524 | Bolkiah | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1582–1598 | Muhammad Hassan | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1828–1852 | Omar Ali Saifuddin II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1885–1906[2] | Hashim Jalilul Alam Aqamaddin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Establishment of the Sultanate | 1368 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Became a British protectorate | 1888 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Barter, Cowrie, Piloncitos, and later Brunei pitis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History of Brunei | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Sultanate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History of Indonesia |
|---|
 |
| Timeline |
In the history of Brunei, the Sultanate of Brunei (Jawi: كسلطانن بروني) or simply Brunei (/bruːˈnaɪ/ broo-NY) was a Malay sultanate, centred in Brunei on the northern coast of Borneo island in Southeast Asia. Brunei became a sovereign state around the 15th century, when it grew substantially after the fall of Malacca to the Portuguese,[3][4] extending throughout coastal areas of Borneo and the Philippines, before it declined in the 17th and 18th centuries.[5] The first ruler or sultan of Brunei was a Muslim. It became a British protectorate in the 19th century.
Historiography
Understanding the history of the old Bruneian Sultanate is quite difficult since it is hardly mentioned in contemporary sources of its time, as well as there being a scarcity of evidence of its nature. No local or indigenous sources exist to provide evidence for any of this. As a result, Chinese texts have been relied on to construct the history of early Brunei.[6] Boni in Chinese sources most likely refers to Western Borneo, while Poli (婆利), probably located in Sumatra, is claimed by local authorities to refer to Brunei as well.[citation needed]
History
Pre-sultanate history
In the 14th century, Brunei seems to be subjected to Java. The Javanese manuscript Nagarakretagama, written by Prapanca in 1365, mentioned Barune as the vassal state of Majapahit,[7] which had to make an annual tribute of 40 katis of camphor.
Expansion
Following the presence of Portuguese after the fall of Malacca, Portuguese merchants traded regularly with Brunei from 1530 and described the capital of Brunei as surrounded by a stone wall.[3][8]
During the rule of Bolkiah, the fifth sultan, the empire held control over coastal areas of northwest Borneo (present-day Brunei, Sarawak and Sabah) and reached Seludong (present-day Manila) and the Sulu Archipelago, including parts of the island of Mindanao.[9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16] In the 16th century, the Brunei empire's influence extended as far as Kapuas River delta in West Kalimantan. The Malay Sultanate of Sambas in West Kalimantan and the Sultanate of Sulu in southern Philippines in particular developed dynastic relations with the royal house of Brunei. Other Malay sultans of Pontianak, Samarinda as far as Banjarmasin, treated the sultan of Brunei as their leader. The true nature of Brunei's relationship with other Malay sultanates of coastal Borneo and the Sulu archipelago is still a subject of study, as to whether it was a vassal state, an alliance, or just a ceremonial relationship. Other regional polities also exercised their influence upon these sultanates. The Sultanate of Banjar (present-day Banjarmasin), for example, was also under the influence of Demak in Java.
Decline
The rising power of the nearby Sultanate of Sulu occurred due to infighting between Bruneian nobles and the king. Brunei eventually lost its authority over the Bajaus and lapsed into a collection of riverine territories ruled by semi-autonomous chiefs.[17]
By the end of 17th century, Brunei entered a period of decline brought on by internal strife over royal succession, colonial expansion of the European powers, and piracy.[5] The empire lost much of its territory due to the arrival of the western powers such as the Spanish in the Philippines, the Dutch in southern Borneo and the British in Labuan, Sarawak and North Borneo. By 1725, Brunei had many of its supply routes had been taken over by the Sulu sultanate.[18]
In 1888, Sultan Hashim Jalilul Alam Aqamaddin later appealed to the British to stop further encroachment.[19] In the same year, the British signed a "Treaty of Protection" and made Brunei a British protectorate,[5] which lasted until 1984, when Brunei gained independence.[20][21]
Government
The sultanate was divided into three traditional land systems known as kerajaan (crown property), kuripan (official property) and tulin (hereditary private property).[22]
References
- ^ Hussainmiya 2010, pp. 67.
- ^ Yunos 2008.
- ^ a b Holt, Lambton & Lewis 1977, pp. 129.
- ^ Andaya & Andaya 2015, pp. 159.
- ^ a b c CIA Factbook 2017.
- ^ Jamil Al-Sufri 2000.
- ^ Suyatno 2008.
- ^ Lach 1994, pp. 580.
- ^ Saunders 2013, pp. 60.
- ^ Herbert & Milner 1989, pp. 99.
- ^ Lea & Milward 2001, pp. 16.
- ^ Hicks 2007, pp. 34.
- ^ Church 2012, pp. 16.
- ^ Eur 2002, pp. 203.
- ^ Abdul Majid 2007, pp. 2.
- ^ Welman 2013, pp. 8.
- ^ Andaya, Barbara Watson (1982). A History of Malaysia. New York: St. Martin's Press. pp. 76–77. ISBN 978-0-312-38120-2.
- ^ de Vienne, Marie-Sybille (2015). Brunei: From the Age of Commerce to the 21st Century. National University of Singapore Press. pp. 39–74. ISBN 9789971698188.
- ^ World Atlas 2017.
- ^ Abdul Majid 2007, pp. 4.
- ^ Sidhu 2009, pp. 92.
- ^ McArthur & Horton 1987, p. 102.
Sources
- Holt, P. M.; Lambton, Ann K. S.; Lewis, Bernard (1977). The Cambridge History of Islam: Volume 2A, The Indian Sub-Continent, South-East Asia, Africa and the Muslim West. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-29137-8.
- Brunei Museum Journal (1986). The Brunei Museum Journal. The Museum of Brunei Darussalam.
- McArthur, M.S.H.; Horton, A.V.M. (1987). Report on Brunei in 1904. Athens, Ohio: Ohio University Center for International Studies, Center for Southeast Asian Studies. ISBN 0-896-80135-7.
- Herbert, Patricia; Milner, Anthony Crothers (1989). South-East Asia: Languages and Literatures : a Select Guide. University of Hawaii Press. ISBN 978-0-8248-1267-6.
- Jamil Al-Sufri, Awang Mohd. Zain (1990). Tarsilah Brunei: sejarah awal dan perkembangan Islam (in Malay). Department of Historical Centre of Ministry of Culture, Youth and Sports of Brunei Darussalam.
- Awang Abdul Aziz bin Awang Juned (1992). Islam di Brunei: zaman pemerintahan Kebawah Duli Yang Maha Mulia Paduka Seri Baginda Sultan Haji Hassanal Bolkiah Mu'izzuddin Waddaulah, Sultan dan Yang Di-Pertuan Negara Brunei Darussalam (in Malay). Department of History of Brunei Darussalam.
- Lach, Donald F. (1994). Asia in the Making of Europe, Volume I: The Century of Discovery. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-46732-0.
- Jamil Al-Sufri, Awang Mohd. Zain (2000). Tarsilah Brunei: The Early History of Brunei Up to 1432 AD. Department of Historical Centre of Ministry of Culture, Youth and Sports of Brunei Darussalam. ISBN 978-99917-34-03-3.
- Lea, David; Milward, Colette (2001). A Political Chronology of South-East Asia and Oceania. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-1-85743-117-9.
- Eur (2002). The Far East and Australasia 2003. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-1-85743-133-9.
- Bala, Bilcher (2005). Thalassocracy: a history of the medieval Sultanate of Brunei Darussalam. School of Social Sciences, Universiti Malaysia Sabah. ISBN 978-983-2643-74-6.
- Hicks, Nigel (2007). The Philippines. New Holland Publishers. ISBN 978-1-84537-663-5.
- Abdul Majid, Harun (2007). Rebellion in Brunei: The 1962 Revolt, Imperialism, Confrontation and Oil. I.B.Tauris. ISBN 978-1-84511-423-7.
- Yunos, Rozan (2008). "The Sultan who thwarted Rajah Brooke". The Brunei Times. Archived from the original on 30 September 2015.
- Suyatno (2008). "Naskah Nagarakretagama" (in Indonesian). National Library of Indonesia. Archived from the original on 23 May 2017. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- History for Brunei Darussalam: Sharing our Past. Curriculum Development Department, Ministry of Education of Brunei Darussalam. 2009. ISBN 978-99917-2-372-3.
- Sidhu, Jatswan S. (2009). Historical Dictionary of Brunei Darussalam. Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-0-8108-7078-9.
- Hussainmiya, B. A. (2010). "The Malay Identity in Brunei Darussalam and Sri Lanka" (PDF). Universiti Brunei Darussalam. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 October 2014.
- Oxford Business Group (2011). The Report: Sabah. Oxford Business Group. ISBN 978-1-907065-36-1.
- Church, Peter (2012). A Short History of South-East Asia. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-118-35044-7.
- Saunders, Graham (2013). A History of Brunei. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-136-87401-7.
- Welman, Frans (2013). Borneo Trilogy Brunei: Vol 1. Booksmango. ISBN 978-616-222-235-1.
- Kurz, Johannes L. (2014). "Boni in Chinese Sources: Translations of Relevant Texts from the Song to the Qing Dynasties" (PDF). Universiti Brunei Darussalam. National University of Singapore. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 May 2014.
- Andaya, Barbara Watson; Andaya, Leonard Y. (2015). A History of Early Modern Southeast Asia, 1400–1830. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-88992-6.
- CIA Factbook (2017). "The World Factbook – Brunei". Central Intelligence Agency.
- World Atlas (2017). "Brunei Darussalam". World Atlas.
Further reading
- Articles with short description
- EngvarB from September 2017
- Use dmy dates from September 2017
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from April 2022
- CS1 Malay-language sources (ms)
- CS1 Indonesian-language sources (id)
- AC with 0 elements
- Former countries in Borneo
- Former countries in Bruneian history
- Former countries in Malaysian history
- Former countries in Philippine history
- Former countries in Indonesian history
- History of Sarawak
- History of Sabah
- Pre-Muslim kingdoms in Malaysian history
- Former empires in Asia
- Former countries
- Former sultanates