Samʼal
 Archeological site of Samʼal | |
| Location | Zincirli Höyük, Gaziantep Province, Turkey |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 37°06′13″N 36°40′43″E / 37.10361°N 36.67861°ECoordinates: 37°06′13″N 36°40′43″E / 37.10361°N 36.67861°E |
| Type | Settlement |
| Site notes | |
| Condition | In ruins |
Samʼal, also Yaʼdiya or Zincirli Höyük, is an archaeological site located in the Anti-Taurus Mountains of modern Turkey's Gaziantep Province. It was founded at least as far back as the Early Bronze Age and thrived between 3000 and 2000 BC, and on the highest part of the upper mound was found a walled citadel of the Middle Bronze Age (2000–1600 BC).[1] New excavations revealed a monumental complex in the Middle Bronze Age II, and another complex that was destroyed in the mid to late 17th century BC, maybe by Hititte king Hattusili I.[2] It was largely abandoned during the Hittite and Mitanni periods but flourished again in the Iron Age, initially under Luwian-speaking Neo-Hittites, and by 920 B.C. had become a kingdom. In the 9th and 8th century BC it came under control of the Neo-Assyrian Empire and by the 7th century BC had become a directly ruled Assyrian province.
History
The site of Samʼal was occupied in the Early Bronze Age (c. 3000-2000 BC), and Middle Bronze Age since c. 2000 until 1650,[1] when it was sacked by Hittite king Hattusili I.
State of Mamma
At least from c.1700 to 1650 BC Zincirli Höyük was a trading hub with the production of wine transported in a specific type of vessel, the globular flask, being part of the trade centered in the ancient Syrian state of Mamma.[3] Zincirli was located only 9 km north of Tilmen Höyük, the capital of the Zalpa/Zalwar kingdom, which eventually became one of the twenty vassal small states of the Yamhad kingdom based on Aleppo.[4] Recent excavations by Chicago-Tubingen Expedition revealed that the supposed bit-hilani palace of Hilani I in Zincirli (believed to be from Iron Age Samʼal period) was actually a large broadroom temple from Middle Bronze Age II, lasting roughly from 1800 to 1650 BC, destroyed in mid- to late 17th century BC.[5] The archaeological site of Zincirli was abandoned after Hattusili I's sack in 1650 BC, but later rose again in the Iron Age, eventually becoming a kingdom. With the rise of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, Samʼal became a vassal state and later a province of that empire.
In 2020, the site was "convincingly identified" with Zalpa, mentioned in the Hittite "Queen of Kanesh" myth.[6]
Kingdom of Samʼal
Kingdom of Samʼal | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1200 BC–609 BC | |||||||||||
| Status | Principality/Kingdom | ||||||||||
| Capital | Samʼal | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Hittite Samalian Aramaic Akkadian | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
• Established | 1200 BC | ||||||||||
• Disestablished | 609 BC | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
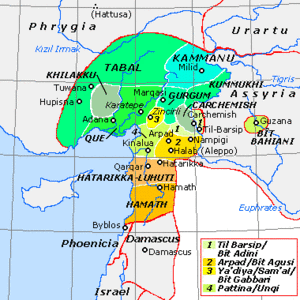
Kingdom of Samʼal (in Samalian Yādiya or Yaʼdiya, in Aramaic Ya'udi) was a middle power of the Middle-East in the first half of the 1st millennium BC. It was near the Nur Mountains. Samʼal was the capital of the country.
The Aramean dynasty founder was king Gabbar, dated around 900 BC. Royal steles and stone tablets from the period of Kilamuwa and Panamuwa II are the main sources for historical data about this time period.
The Kilamuwa Stela is a 9th-century BC stele of King Kilamuwa found in Sam'al, and written in Phoenician language. It is written in an Old Aramaic form of the Phoenician alphabet, and was found in 1902.
Also the Kilamuwa scepter has been found here in 1943. It is a small gold object inscribed in a similar old type of Phoenician alphabet.[7]
The kingdom became a middle power at the end of the 10th century BC. It had expanded from being a city state and gained territories from Carchemish, around Adana from Quwê and remained independent. It didn't become part of Cilicia. In 859 BC Alimus was saved with the help of Hayyanu, king of Samʼal. He didn't participate in the Battle of Qarqar in 853 BC, but Assyria had been blocked in the Western area. Though the campaign of Assyria in 825 BC occupied the vital territories of Samʼal, Quwê had been defeated, but it had been reorganised as Denyen. After the death of Shalmaneser III, Ya'udi again became independent.
Some rulers of Samʼal had aggressive expansionist politics; others acceded to one of the anti-Assyrian Syrian coalition. Assyrian sources are not clear regarding Samʼal. Ya'udi was one of Assyria's satellite states in the annals of Shalmaneser III. Though around 830 BC Azitawadda, king of Denyen, states Ya'udi is his satellite country – at the same time, Kilamuwa mentions on his stela that he hired Assyria against Denyen. Other sources from the same period mention Ya'udi as a satellite state of Denyen and Assyria wanted to occupy this territory. Kilamuva might offer for Deyen to be a satellite state. Before this, he should defeat his greatest foe, Azitawadda. Assyrians won over Denyen and Samʼal in 825 BC. Samʼal became independent after the death of Shalmaneser III.
There is an alternative opinion which states that Ya'udi and Samʼal were originally separate royal houses and Samʼal, the younger of the two, fought against the Assyrians at Alimus in 859 BC, in 858 BC when Shalmanser III crossed the Euphrates for the first time, and again in 853 BC at the Battle of Qarqar. The Kingdom of Samʼal was founded by Hayyanu and his successor was Ahabbu of Siri'laya (Zincirli) in 854 BC. Whereas Gabar, the founder of Ya'udi, and his successors became a member of the Assyrian satellites. This makes clear why Shalmaneser III lists Ya'udi (Bit-Gabbari) but not Samʼal as a satellite state. The Kingdom of Ya'udi wanted to open a corridor between Assyria and Denyen. It was prevented by the unified Syrian forces. This unity had been dissolved in 825 BC. After the death of Shalmanezer III Denyen couldn't occupy it but the Samalians could. Samʼal annexed Ya'udi and moved into the palace of Kilamuva.
At the end, in 717 BC, Assyria occupied the country under the rule of Sargon II.
Archaeology
The site was excavated in 1888, 1890, 1891, 1894 and 1902 during expeditions led by Felix von Luschan and Robert Koldewey. Each of the expeditions was supported by the German Orient Committee, except for the fourth (1894), which was financed with monies from the Rudolf-Virchow-Stiftung and private donors.[8] There were five excavation reports:
- Volume 1: Felix von Luschan et al, Ausgrabungen in Sendschirli: Einleitung und Inschriften, Spemann, 1893
- Volume 2: Felix von Luschan and Carl Humann and Robert Koldewey, Ausgrabungen in Sendschirli: Ausgrabungsbericht und Architektur, Spemann, 1898
- Volume 3: Felix von Luschan, Ausgrabungen in Sendschirli: Thorsculpturen, Georg Reimer, 1902
- Volume 4: Felix von Luschan and Gustav Jacoby, Ausgrabungen in Sendschirli, Georg Reimer, 1911
- Volume 5: Felix von Luschan and Walter Andrae, Ausgrabungen in Sendschirli: Die Kleinfunde von Sendschirli, Walter de Gruyter, 1943
They found a heavily fortified teardrop-shaped citadel, which was surrounded by the as yet unexcavated town and a further enormous double fortification wall with three gates and 100 bastions.
The field diaries of the excavation were lost during World War II.
In August 2006, the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago together with the Institute for Ancient Near Eastern Studies of the University of Tübingen began a new long-term excavation project at the site of Zincirli under the directorship of David Schloen. Eight seasons of excavation have been conducted through 2015.[9] [10] [11] [12]
Lions
Among the notable objects found at the site are five giant statues of lions carved from stone, known as the Samʼal lions, which apparently had guarded the gates of the city, but may have been ritually buried together within the citadel.
Inscriptions found in the area
Multiple important historical inscriptions have been found in this area. They include at least seven inscriptions, as listed at the link above, including the Kuttamuwa stele found in 2008.
The German excavations on the citadel recovered large numbers of relief-carved orthostats, along with inscriptions in Aramaic, Phoenician, and Akkadian. These are on exhibit in the Pergamon Museum, Berlin, and Istanbul. Also found was the notable Victory stele of Esarhaddon celebrating his victory over Taharqa.
Three royal inscriptions from Ya'udi or Samʼal are particularly informative for the history of the area. The earliest is from the reign of King Panammu I, the others later at 730 BC. Their language is known as Samalian or Ya'udic. Some scholars including P.-E. Dion[13] and S. Moscati[14] have advanced Samalian as a distinct variety of Old Aramaic.[15][16][17] Attempts to establish a rigorous definition of "Aramaic" have led to a conclusion of Samalian as distinct from Aramaic, despite some shared features.[18][19][20]
Pancarli Hoyuk inscription
The site of Pancarli Hoyuk is located about 1 km southeast of Zincirli. A new hieroglyphic Luwian inscription has been discovered here in 2006, and published in 2016.[21]
The inscription is fragmentary, but nevertheless it appears to be of a royal character. Previously, all known inscriptions from this area were exclusively written in West Semitic languages. According to the authors, the most probable conclusion is that PANCARLI inscription represents a ruler or a local king of the tenth or early ninth century BC.[21]
This inscription provides new information about the Early Iron Age of the Islahiye valley, and the history of the Aramaean dynasty of Gabbar.
If the inscription is considered to date to the 10th century BC, it may be the first solid evidence for a Luwian-speaking kingdom in the Islahiye valley, as possibly an offshoot of the Hittite rump-state at Karkemish.[21]
Gallery
Kilamuwa Stela: an inscription of Prince Kilamuwa of Samal, Pergamon Museum
Hadad Statue with inscription (KAI 214), Pergamon Museum
Panamuwa II inscription (KAI 215)
Bar-Rakib stele I (KAI 216), Istanbul Museum
Bar-Rakib stele III (KAI 218), Pergamon Museum
Stele of Ördek-Burnu in the Istanbul Museum of the Ancient Orient
Notes
- ^ a b Chicago-Tubingen Expedition to Zincirli, (2018). "Site and Setting", The University of Chicago.
- ^ Herrmann, Virginia, et al., (2020). "Iron Age Urbanization and Middle Bronze Age Networks at Zincirli Höyük: Recent Results from the Chicago-Tübingen Excavations", in ASOR 2020 Annual Meeting.
- ^ Morgan, Kathryn R., and Seth Richardson, (2020). "Wine from Mamma: Alluharum-Pots in 17th Century BC Trade Networks", Iraq journal, Cambridge University Press, pp. 1-27.
- ^ Turkish Archaeological News, (9 March 2019). "Tilmen Höyük": "...Bahadir Alkım, in turn, hypothesised that Tilmen Höyük [Zalpa/Zalwar] was the capital of one of the twenty small states that together formed the kingdom of Yamhad..."
- ^ Virginia R. Herrmann and David Schloen, "Middle Bronze Age Zincirli: The Date of "Hilani I" and the End of Middle Bronze II", Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, vol. 385, pp. 33–51, May 2021
- ^ The University of Chicago, (2018). "Annals of Ḫattušili I (mid- to late 17th cent. BC)", in Chicago-Tubingen Expedition to Zincirli, Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ Editio princeps: Felix von Luschan, Die Kleinfunde von Sendschirli . Herausgabe und Ergänzung besorgt von Walter Andrae (Mitteilungen aus den orientalischen Sammlungen, Heft XV; Berlin 1943) 102, Abb. 124, Tf. 47f-g (the book was reviewed by K. Galline; in BiOr 5 fl948] 115–120)
- ^ Felix von Luschan, "Ueber einige Ergebnisse der fünften Expedition nach Sendschirli," Zeitschrift für Ethnologie 34 (1902): 379–80.
- ^ J. David Schloen and Amir S. Fink, New Excavations at Zincirli Höyük in Turkey (Ancient Samʼal) and the Discovery of an Inscribed Mortuary Stele, Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, vol. 356, pp. 1-13, November 2009
- ^ [1][dead link] Schloen, J David; Fink, Amir S., SEARCHING FOR ANCIENT Samʼal: NEW EXCAVATIONS AT ZINCIRLI IN TURKEY, Near Eastern Archaeology, Vol. 72, Iss. 4, pp. 203-219, 2009
- ^ [2] Virginia R. Herrmann and David Schloen, EXCAVATIONS AT ZINCIRLI HÖYÜK IN TURKEY: 2015 SEASON, Oriental Institute of Chicago, 2016
- ^ Kathryn R. Morgan and Sebastiano Soldi, "Middle Bronze Age Zincirli: An Interim Report on Architecture, Small Finds, and Ceramics from a Monumental Complex of the 17th Century b.c.e.", Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, vol. 385, pp. 33–51, May 2021
- ^ P.-E. Dion, La langue de Ya'udi (Waterloo, Ontario 1974), in: RSO 53 (1979)
- ^ Moscati 1964, S.—: An Introduction to the Comparative Grammar of the Semitic Languages, Harrassowitz, Wiesbaden.
- ^ Klaus Beyer The Aramaic Language, Its Distribution and Subdivisions 1986- Page 12 3525535732 "In addition the three "Ya'udic" royal inscriptions from Zinjirli in northern Syria (c. 825, 750, 730 B.C.) witness to early Ancient Aramaic: KAl 25, 214, 215; TSSI -, 13, 14; J.Friedrich, Phoni- zisch-punische Grammatik, Rome 1951, 153-162; ..."
- ^ Angel Sáenz-Badillos, John Elwolde A History of the Hebrew Language 1996 0521556341 Page 35 "According to some scholars, after 1400 BC the languages which would later develop into Ya'udic and Aramaic...."
- ^ Joseph A. Fitzmyer A Wandering Armenian: Collected Aramaic Essays 1979 - Page 68 080284846X "This is partly because he refuses to see Ugaritic as Canaanite and partly because he prefers to treat so-called Ya^udic as distinct from Aramaic — if I understand him correctly.89 "
- ^ Huehnergard, John (1995). "What is Aramaic?". ARAM Periodical. 7 (2): 261–282. doi:10.2143/ARAM.7.2.2002231.
- ^ Kogan, Leonid (2015). Genealogical Classification of Semitic. de Gruyter.
- ^ Pat-El, Na'ama; Wilson-Wright, Aren (2019). "The subgrouping of Samalian: Arguments in favor of an independent branch". Maarav. 23 (2): 371–387.
- ^ a b c Herrmann, Virginia R.; van den Hout, Theo; Beyazlar, Ahmet (2016). "A New Hieroglyphic Luwian Inscription from Pancarlı Höyük: Language and Power in Early Iron Age Samʾal-YʾDY". Journal of Near Eastern Studies. University of Chicago Press. 75 (1): 53–70. doi:10.1086/684835. ISSN 0022-2968.
See also
- Cities of the ancient Near East
- Short chronology timeline
- Euphrates Syrian Pillar Figurines
- Euphrates Handmade Syrian Horses and Riders
References
- Jessie DeGrado and Madadh Richey, "An Aramaic-Inscribed Lamaštu Amulet from Zincirli", Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, vol. 377, pp. 107–133, May 2017
- Simon B. Parker (1996). "Appeals for military intervention: stories from Zinjirli and the Bible". The Biblical Archaeologist 59(4): 213-224.
- Ussishkin, David (1970). "The Syro-Hittite ritual burial of monuments". Journal of Near Eastern Studies 29(2): 124-128.
- Ralf-B Wartke, Samʼal: Ein aramäischer Stadtstaat des 10. bis 8. Jhs. v. Chr. und die Geschichte seiner Erforschung, Philipp von Zabern, 2005
- J. P. Francev, ed. (1967). Világtörténet tíz kötetben, I. kötet (in Hungarian). Kossuth K.
- U. Bahadir. Alkim, The Road from Samal to Asitawandawa: Contributions to the Historical Geography of the Amanus Region, Anadolu Arastirmalari, vol. 2, pp. 3–41, 1965
- Dennis Pardee, A New Aramaic Inscription from Zincirli, Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, vol. 356, pp. 51–71, 2009
- David Schloen, J. and Amir S. Fink, Searching for Ancient Samal: New Excavations at Zincirli in Turkey, Near Eastern Archaeology, vol. 72/4, pp. 203–219, 2009
- Eudora J. Struble and Virginia Rimmer Herrmann, An Eternal Feast at Sam?al: The New Iron Age Mortuary Stele from Zincirli in Context, Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, vol. 356, pp. 15–49, 2009
- VR Herrmann, Urban organization under empire: Iron Age Sam'al (Zincirli, Turkey) from royal to provincial capital, Levant, vol. 49 (3), pp. 284–311, 2017
External links
 Media related to Samʼal at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Samʼal at Wikimedia Commons- Official Zincirli Excavation Website at www.uchicago.edu
- ASOR 2015 dig video
- Plans and fotos at www.hittitemonuments.com
- Levy-White project to publish small finds from German excavations
- The Aramean Kingdoms of Samʼal
- Ancient Aramaic Incantation Describes 'Devourer' that Brings 'Fire' to Victims
- All articles with dead external links
- Articles with dead external links from July 2022
- Articles with short description
- Coordinates not on Wikidata
- CS1 Hungarian-language sources (hu)
- Commons category link is the pagename
- AC with 0 elements
- Archaeological sites in Southeastern Anatolia
- Hittite cities
- Ancient Assyrian cities
- Aramean cities
- Aramean states
- Syro-Hittite states
- Former populated places in Turkey
- States and territories established in the 12th century BC