Military macaw
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2017) |
| Military macaw | |
|---|---|

| |
| A military macaw at the London Zoo | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Psittaciformes |
| Family: | Psittacidae |
| Genus: | Ara |
| Species: | A. militaris
|
| Binomial name | |
| Ara militaris (Linnaeus, 1766)
| |
| |
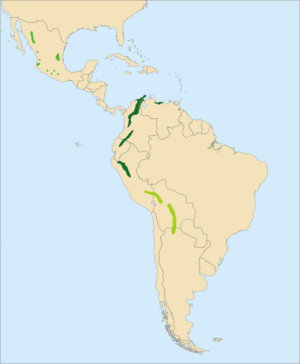
| Distribution of the 3 subspecies of military macaw | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Psittacus militaris Linnaeus, 1766 | |
The military macaw (Ara militaris) is a large parrot and a medium-sized macaw that gets its name from its predominantly green plumage resembling a military parade uniform. It is native to forests of Mexico and South America and though considered vulnerable in the wild, it is still commonly found in the pet trade industry.
Taxonomy
The military macaw was formally described in 1766 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the twelfth edition of his Systema Naturae. He placed it with all the other parrots in the genus Psittacus and coined the binomial name Psittacus militaris.[3] Linnaeus did not specify a type locality but this was designated as Colombia in 1912.[4][5] The military macaw is now one of ten parrots placed in the genus Ara which was erected in 1799 by the French naturalist Bernard Germain de Lacépède.[6][7] The genus name is from ará meaning "macaw" in the Tupi language of Brazil. The word is an onomatopoeia based on the sound of their call. The specif epithet militaris is Latin meaning "military".[8]
Three subspecies are recognised:[7]
- A. m. mexicanus Ridgway, 1915 – west Mexico
- A. m. militaris (Linnaeus, 1766) – Colombia, northwest Venezuela, Ecuador, north, southeast Peru and northwest Bolivia
- A. m. bolivianus Reichenow, 1908 – central Bolivia and northwest Argentina
Description
The military macaw is 70 to 85 centimeters (27.5 to 33.5 inches) long on average, and 99–110 cm (33–43 in) across the wings. Military macaws are mostly green with light blue and yellow flight and tail feathers and a bright red patch on their forehead. Their face is bare and white in color with black striations. The large strong beak is grey-black and the iris is yellow.
They greatly resemble great green macaws and are usually distinguished from great green macaws by their smaller size, completely black bill, and overall darker color.[9] They can also be separated by differences in vocalization and the tendency for great green macaws to be a humid forest species while military macaws are usually a deciduous forest species.[9] Phylogenetic studies have shown that the two species are sister clades.[9]
The subspecies differ in size and plumage.[9] The difference in size is generally 70–80 cm (28–31 in), with the militaris subspecies being the smallest and the mexicana being the largest.[citation needed]
Behavior
Military macaws live in large flocks and can live about 50–60 years in the wild. They can often be heard long before they are seen. They are a very noisy bird making a variety of loud cracking and shrieking sounds, including a loud kraa-aak.[citation needed] Military macaw activity has been observed most frequently in the morning and the evening meaning they are most likely a crepuscular species.[10]
Food and feeding
Military macaws will leave their roosts in flocks around dawn to forage.[11] Their diet consists of mostly seeds but also includes fruits and leaves.[11] They have been observed using Pseudalcantarea grandis for water and consuming latex from Plumeria rubra.[11] They have a somewhat narrow diet meaning that they only eat a small percentage of species of plants that are available to them.[11]
They will also visit heaps of clay known as "macaw licks". These clay licks are found along riverbanks or sometimes in the interior of the Amazon rainforest. Macaws will flock to there to feed on these clay deposits, which appear to detoxify the poisons found in the seeds and vegetation of the rest of their diet. It is also thought that this clay provides the macaws with dietary salt not available in their normal diet.[citation needed]
Breeding

Pair-bonding behaviors include grooming and regurgitation and has been observed during breeding and non-breeding periods.[12] Courtship will occur as early as March, while copulation doesn't actually take place until May and July.[13] Breeding season is typically between March and October while incubation and hatching occurs during August and September.[13] The reproductive season begins with nest selection around October and ends when the chicks fledge between January and March.[12] Military macaws are cavity-nesters and will nest in natural cavities such as holes in trees or on cliffs.[14][12][13] They nest in trees at least 15 meters tall and 90 centimeters wide.[15] During breeding season, the male will feed the female 3-4 times a day.[12]
Distribution and habitat


Military macaws typically inhabit tropical deciduous and semi-deciduous forests.[10] They are a canopy species because they require large canopy trees of deciduous and subdeciduous forests for feeding, breeding, and nesting behavior.[15] They also use canopy trees for protection from predators and heat.[15] They typically live at elevations of 600 to 2600 m, higher in the mountains than most macaws ever range. However, these macaws may seasonally fly down to lowlands, where they are likely in humid forests and thorny woodlands. They will nest in the tops of trees and more often in cliff-faces over 600 ft. (200 m) above the ground.[citation needed]
The three subspecies of the military macaw are distinguished geographically. A. m. militaris are found in areas of Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela. A. m. mexicana occupy areas in Mexico and A. m. boliviana live in Bolivia and Argentina.[7]
The military macaw has escaped or been deliberately released in to Florida, USA, but there is no evidence that the population is breeding and may only persist due to continuing releases or escapes.[citation needed]
Conservation status
Military macaws are estimated to only have a breeding population of 2000-7000 individuals and is continuing to decrease.[16] According to the ICUN red list, military macaws are listed as vulnerable as they face threats from habitat loss due to crops, deforestation, mining, and roads, with already extremely fragmented populations.[16] A 2013 paper found that the habitat for populations in tropical dry forests has been reduced by almost 32%.[15] Military macaws are listed as CITES Appendix 1 which means commercial international trade in wild specimens is prohibited.[17] Despite this, research shows that the trafficking of parrots from South America to North America is still common.[17]
Their narrow diet is also of concern. If the environment were to take a hit and they lost access to too many of their diet species, the species could be greatly affected.[11] There is promise however in that they have a less narrow diet during certain times of the year showing that they may have the ability to adapt if they did lose their typical diet species.[11]
Another conservation concern may be genetic diversity. Military macaws actually have moderate genetic diversity despite their small population, which points to a large ancestral population.[18] Though they have moderate genetic diversity, they are still risk of population bottlenecks due to habitat fragmentation and inbreeding.[18]
Gallery
Eating at Disney's Animal Kingdom, Florida
Military macaw alongside scarlet macaw in Morelia, Mexico
Resting in the Tropical Zone of the Montreal Biodome
Cougar Mountain Zoo Issaquah, WA
References
- ^ BirdLife International (2020). "Ara militaris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T22685548A179407584. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22685548A179407584.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 2022-01-14.
- ^ Linnaeus, Carl (1766). Systema naturae : per regna tria natura, secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis (in Latin). Vol. 1, Part 1 (12th ed.). Holmiae (Stockholm): Laurentii Salvii. p. 139.
- ^ Brabourne, W.; Chubb, C. (1912). The Birds of South America. London: R.H. Porter. p. 80.
- ^ Peters, James Lee, ed. (1937). Check-List of Birds of the World. Vol. 3. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. p. 181.
- ^ Lacépède, Bernard Germain de (1799). "Tableau des sous-classes, divisions, sous-division, ordres et genres des oiseux". Discours d'ouverture et de clôture du cours d'histoire naturelle (in French). Paris: Plassan. p. 1. Page numbering starts at one for each of the three sections.
- ^ a b c Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (January 2022). "Parrots, cockatoos". IOC World Bird List Version 12.1. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 23 March 2022.
- ^ Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. pp. 52, 255. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ^ a b c d Eberhard, Jessica R.; IñIgo-Elias, Eduardo E.; Enkerlin-Hoeflich, Ernesto; Cun, E. Paùl (December 2015). "Phylogeography of the Military Macaw (Ara militaris) and the Great Green Macaw (A. ambiguus) based on mtDNA sequence data". The Wilson Journal of Ornithology. 127 (4): 661–669. doi:10.1676/14-185.1. ISSN 1559-4491.
- ^ a b Bonilla-Ruz, Carlos; Reyes-Macedo, Gladys; García, Rufina (December 2007). "Observations of the Military Macaw (Ara militaris) in Northern Oaxaca, México". The Wilson Journal of Ornithology. 119 (4): 729–732. doi:10.1676/06-116.1. ISSN 1559-4491.
- ^ a b c d e f Contreras-González, A. M.; Rivera-Ortíz, F. A.; Soberanes-González, C.; Valiente-Banuet, A.; Arizmendi, M. C. (June 2009). "Feeding ecology of Military Macaws (Ara militaris) in a semi-arid region of central México". The Wilson Journal of Ornithology. 121 (2): 384–391. doi:10.1676/08-034.1. ISSN 1559-4491.
- ^ a b c d Rivera-Ortíz, Francisco A.; Oyama, Ken; Villar-Rodríguez, Carlos L.; Contreras-González, Ana M.; Arizmendi, María del Coro (2016-06-01). "The use of tree cavities and cliffs by the Military Macaw (Ara militaris) in Salazares Nayarit, Mexico". Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad. 87 (2): 540–544. doi:10.1016/j.rmb.2016.02.002. ISSN 1870-3453.
- ^ a b c Rivera-Ortíz, Francisco; Contreras-González, Ana; Soberanes, Carlos; Valiente-Banuet, Alfonso; María; Arizmendi, Maria (2008-02-10). "Seasonal abundance and breeding chronology of the military macaw (Ara militaris) in a semi-arid region of central Mexico". Ornitologia Neotropical. 19: 255–263.
- ^ de la Parra-Martínez, Sylvia Margarita; Renton, Katherine; Salinas-Melgoza, Alejandro; Muñoz-Lacy, Luis Guillermo (2015-04-01). "Tree-cavity availability and selection by a large-bodied secondary cavity-nester: the Military Macaw". Journal of Ornithology. 156 (2): 489–498. doi:10.1007/s10336-014-1150-9. ISSN 2193-7206.
- ^ a b c d Rivera-Ortíz, Francisco A.; Oyama, Ken; Ríos-Muñoz, César A.; Solórzano, Sofía; Navarro-Sigüenza, Adolfo G.; Del Coro Arizmendi, María (2013-12-01). "Habitat characterization and modeling of the potential distribution of the Military Macaw (Ara militaris) in Mexico". Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad. 84 (4): 1200–1215. doi:10.7550/rmb.34953. ISSN 1870-3453.
- ^ a b "The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved 2019-11-21.
- ^ a b Herrera, Mauricio; Hennessey, Bennett (December 2007). "Quantifying the illegal parrot trade in Santa Cruz de la Sierra, Bolivia, with emphasis on threatened species". Bird Conservation International. 17 (4): 295–300. doi:10.1017/S0959270907000858. ISSN 1474-0001.
- ^ a b Rivera-Ortíz, Francisco A.; Solórzano, Sofía; Arizmendi, María del C.; Dávila-Aranda, Patricia; Oyama, Ken (2017-01-01). "Genetic Diversity and Structure of the Military Macaw (Ara militaris) in Mexico: Implications for Conservation". Tropical Conservation Science. 10: 1940082916684346. doi:10.1177/1940082916684346. ISSN 1940-0829.
External links
- Military macaw photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- "Military macaw media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Audio recordings of Military macaw on Xeno-canto.
Error: "Q838924" is not a valid Wikidata entity ID.
- CS1: long volume value
- CS1 Latin-language sources (la)
- CS1 French-language sources (fr)
- Articles with short description
- Articles needing additional references from February 2017
- All articles needing additional references
- IUCN Red List vulnerable species
- Articles with 'species' microformats
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Articles with unsourced statements from January 2020
- Articles with unsourced statements from April 2020
- Taxonbars desynced from Wikidata
- Taxonbar pages requiring a Wikidata item
- Taxonbars with invalid from parameters
- Taxonbars without secondary Wikidata taxon IDs
- Ara (genus)
- Macaws
- Birds of Mexico
- Birds of the Northern Andes
- Birds of the Sierra Madre Occidental
- Birds described in 1766
- Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus
- Articles containing video clips
- Species endangered by the pet trade
- Species endangered by deforestation
- Birds of the Sierra Madre del Sur
- Birds of the Sierra Madre Oriental
- Birds of the Yungas






