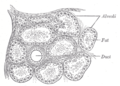
Alveolar gland
| Alveolar gland | |
|---|---|
 Section of pancreas of dog. X 250. | |
| Anatomical terminology |
If glands are categorized by shape, alveolar glands contrast with tubular glands. Alveolar glands have a saclike secretory portion, and are also termed saccular glands. They typically have an enlarged lumen (cavity), hence the name similar to alveoli, the very small air sacs in the lungs.
Some sources draw a clear distinction between acinar and alveolar glands, based upon the size of the lumen.[1] A further complication in the case of the alveolar glands may occur in the form of still smaller saccular diverticuli growing out from the main sacculi.
The term "racemose gland"[2] is used to describe a "compound alveolar gland" or "compound acinar gland."[3]
Branched alveolar glands are classified as follows:
| Type | Description | Location | |
|---|---|---|---|

|
simple branched acinar |
thyroid glands | |

|
tubuloalveolar or tubulo-alveolar or tubulo-acinar or compound tubulo-acinar or compound tubuloalveolar[4] |
glands that start out as simple branched tubular, and branch further to terminate in alveoli | salivary glands,[5] esophagus[6] mammary glands |
Additional images
Human submaxillary gland. At the right is a group of mucous alveoli, at the left a group of serous alveoli.
Section of portion of mamma.
See also
References
- ^ Classification of Exocrine Glands
- ^ Racemose+gland Archived 2012-10-13 at the Wayback Machine at eMedicine Dictionary
- ^ SIU SOM Histology GI
- ^ Histology at KUMC glands-glands17
- ^ Histology at KUMC glands-glands14 "Compound Tubulo- Alveolar"
- ^ MedEd at Loyola histo/practical/epithelium/hp1-28.html