Glycine betaine aldehyde
(Redirected from Betaine aldehyde)
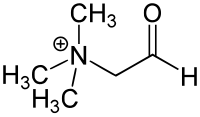
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N,N-Trimethyl-2-oxoethan-1-aminium | |
| Other names
Betaine aldehyde
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12NO | |
| Molar mass | 102.157 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Glycine betaine aldehyde, often simply called betaine aldehyde,[1] is an intermediate in the metabolism of glycine, serine and threonine. The human aldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.3) stimulates the transformation of betaine aldehyde to glycine betaine. Betaine aldehyde is a substrate for choline dehydrogenase (mitochondrial).[2]
Chemical structure
Glycine betaine aldehyde is a short chain aldehyde and quaternary ammonium compound. It can be considered a derivative of the amino acid glycine. Its chemical formula is C5H12NO+.
Biological function
Glycine betaine aldehyde is a component of glycine, serine and threonine metabolism. It also serves as an osmolyte.
It can be found in cytoplasm and mitochondria within the kidney, neurons, and stratum corneum.[3]
References
- ^ Betaine aldehyde Archived 2007-11-24 at the Wayback Machine, Biological Magnetic Resonance Data Bank
- ^ Yilmaz JL, Bülow L. (December 2002). "Enhanced stress tolerance in Escherichia coli and Nicotiana tabacum expressing a betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase/choline dehydrogenase fusion protein". Biotechnol. Prog. 18 (6): 1176–82. doi:10.1021/bp020057k. PMID 12467448. S2CID 8054758.
- ^ Metabocard for Dimethylglycine, Human Metabolome Database
Categories:
- Webarchive template wayback links
- Chemical articles with multiple compound IDs
- Multiple chemicals in an infobox that need indexing
- Chemical articles with multiple CAS registry numbers
- Pages using collapsible list with both background and text-align in titlestyle
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chembox image size set
- Articles with short description
- Aldehydes
- Quaternary ammonium compounds